Osteoarthritis – bulk package dystrophic-degenerative joint diseases, different clinical and morphological localization and Etiology and exodus of the machine this similar image and manifested lesions articular cartilage, subchondral bone formations, capsules, fiber apparatus.
Osteoarthritis is the most common pathology, rheumatology practice, according to medical statistics, only 1/5 part of the population is until you've got them. Cause a significant reduction in the quality of life of osteoarthritis, approximately half of the patients, a large proportion are incapable of. The incidence depends on age: osteoarthritis is a rare, beginning at a young age after 40-45 years most often, this radiological findings in people over the age of 70, definitions, in most cases. At a young age, the incidence was approximately 6.5%, 45 years later – 14-15%, 50 years later, – 27-30%, of individuals who are over the age of 70 to 80 to 90%.
The most common pathological process of osteoarthritis small joints of the brush (women 10 times more often in men), thumb, intervertebral joints, cervical spine and orange sections and knee and hip joints. Osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joints the ranks of clinical symptoms and the severity of adverse effects quality of life.
Auxiliary devices typical of osteoarthritis joints and burning for a comprehensive defeat:
- inflammatory changes in cartilage, articular;
- subject to a pathological process of involvement of bone structures;
- synovitis – inflammation of the joint capsule, internal shell;
- bursitis – defeat bag approximately joints;
- inflamed soft tissue reactance (Nov, subcutaneous tissue, fiber apparatus) in the distance from the projection of the affected joint.
The root cause inflammatory changes in osteoarthritis because a number of Western countries called disease, arthritis. Arthritis and osteoarthritis with equal frequency in men Russian medical terminology, and implication, the same pathological process. Recently the term most commonly used in practice, rheumatology, osteoarthritis, emphasizing involvement in a pathological process, not just a moving connection such as a real joint, but also bone formations that comprise it.
The results in the absence of osteoarthritis, treatment is sufficient, a reduction gradually progressive movements, immobilization of the affected joints.
An understanding of currently the approach has changed significantly in osteoarthritis: a disease is considered a violent inflammation of the joints cartilage destruction process that requires mandatory under the influence of active anti-inflammatory treatment.
Synonyms: arthritis, osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis of corruption.
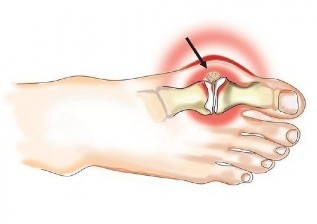
Causes and risk factors
Within the scientific community conducted a discussion of the root causes of joint involvement. Some researchers assign an important role to articular cartilage damage under the influence of the surface coating and the various factors that leads to dystrophic changes in joint biomechanics the violation to the surrounding structures. Others, on the contrary, to see the bone structures that make up the mating joints for Root lesion surface layer (for example, because of a violation micro) and consider changes in the secondary cartilage degeneration and dystrophy.
Promote the development of osteoarthritis, the most common of the causal factors:
- acute traumatic joint injury previous (a space or sprains, bruises, dislocations, intra-articular fractures, a wounded penetrating);
- the load that is related to a particular systematic extreme activity (professional athletes, dancers, people in question, heavy physical labor, etc.);
- obesity;
- local cold exposure;
- chronic diseases, which have local microcirculation (endocrine pathology, pathology of the vascular bed, etc.);
- acute infectious disease that is passed;
- changes of a hormonal background (pregnancy, menopause);
- autoimmune diseases, connective tissue damage to the implied;
- connective tissue dysplasia (a congenital weakness of this type of tissue, together with increased mobility and joints);
- genetic pathology – gene defect localized to chromosome 12 and encoding a collagen Pro Type II (COL2A1) gene or the controller VDR vitamin D-endocrine system;
- structural and functional abnormalities congenital joint apparatus;
- mature, elderly and senile age;
- vacuum bone loss (osteoporosis);
- chronic poisoning (including alcohol);
- passed joint operational intervention.
In most cases, the nature of the causes of osteoarthritis include being poly, i.e., developing the combined effects of several causative factors.
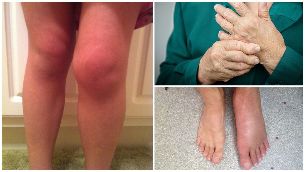
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
Not for osteoarthritis, which is characterized by acute clinical picture, the changes in the joints are worn, progressive, gradually increasing the air, slowly rising symptoms:
- pain;
- the crisis that emerged in the affected joints from time to time;
- joint deformity, and increased as it progresses and crop diseases;
- hardness;
- limited mobility (volume reduction of joint active and passive movements of the affected joint).
Idiot wears the temporary nature osteoarthritis pain, visible movement in the background with a heavy load, the end of the day (maybe it's not so intense that many patients sleep). It's not permanent, mechanical and uncharacteristic for a character indicative active inflammation pain osteoarthritis (subchondral bone, synovial membrane, joint, or fiber apparatus the circumference of Nov).
Most of the patients notes the existence of the so-called initial pain, waking up in the morning or after a long idle period after the last developing during motor activity. Many patients in this situation only as a necessity "joint development" or "incompatibility".
Localization and stiffness of osteoarthritis, which is characterized by net for a short duration (30 minutes), I feel sick sometimes perceived that the "jelly" joint. Perhaps the tightness, stiffness.
During development, the main symptoms of joint synovitis in reactive align:
- pain and local temperature rise, defined joint on palpation;
- persistent pain;
- increased joint volume, soft tissue swelling;
- a progressive reduction of movements.
The volume increase for the typical osteoarthritis of the joint, soft tissue swelling.
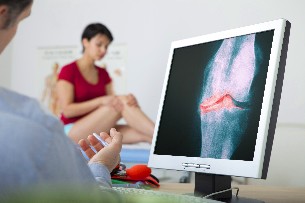
Diagnosis
Osteoarthritis diagnosis based on the evaluation of anamnestic data, characteristic symptoms, the results of instrumental research methods. General and biochemical analysis of blood for osteoarthritis are characterized by exponential change, not an inflammatory process active in the development as they appear.
A main instrumental diagnostic methods of osteoarthritis, radiography, or magnetic resonance tomography the computer that holds these diagnostic advice in ambiguous situations.
Osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joints the ranks of clinical symptoms and the severity of adverse effects quality of life.
Additional diagnostic methods:
- arthroscopy;
- ultrasonography (points, thickness of cartilage, synovium, joint bags the situation, the state, liquid);
- scintigraphy (standings, bone head, bone, joint forming).
Treatment of osteoarthritis
Medicine treatment etc..:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, – severe symptoms of pain and inflammation, acute;
- glucocorticosteroid hormones – intra-articular injection synovitis of events for the introduction of edema; current, in limited circumstances, in the shortest time necessary to resolve the symptoms;
- antufermutral tools (proteolizis inhibitors) – prevent progression of cartilage and bone tissue and degenerative and dystrophic processes;
- antispazmodik are allow to eliminate local spasm of accommodation available Nov a damaged;
- anabolic drugs accelerates regeneration of damaged tissue;
- drugs aimed at correcting properties, strengthening the blood vessel walls, increasing elasticity and tissue regeneration – promoting riverbed mikrozirkulation the blood vessel walls, providing sufficient blood flow to damaged area;
- the developed micro-tool;
- drugs, Joint them, despite being a large distribution, treatment, arthritis, large, placebo-controlled clinical efficacy trials, this group of drugs is not proven.
Methods of physiotherapy treatment of osteoarthritis:
- Ankara Regional Nov, enhance blood circulation and to attract local spasm;
- active kinesiotherapy exercise, so that during osteoarthritis by using custom simulators;
- osteoarthritis during gymnastics;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound treatment;
- therapy baths, mud, paraffin; etc.
The ineffectiveness of the methods listed effects, if any, remedy complications, surgical treatment osteoarthritis:
- meta pineal and bone in the long term a block decompression (reduction of pressure on the affected area of bone);
- corrective osteotomy;
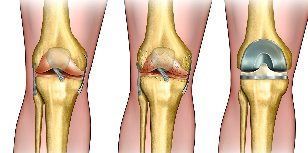
- arthroplasty joint.
Applied mechanics in the early stages of the disease, the laser apparatus (smooth surface removing damaged cartilage lifeless plots). This method effectively eliminates pain syndrome, but temporary effect in 2-3 years.
Possible complications and consequences
The results of osteoarthritis, particularly of the treatment is sufficient is:
- progressive reduction of movements in the affected joints;
- immobilization.
Guess
The estimated life is conducive to. Ugur social and employment forecasts depends on timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease, while surgical treatment to correct the problem is reduced to if necessary.
Prevention
- Waiver of intense stress, long-term static voltage of the affected joint.
- Wearing orthotics if needed.
- Osteoarthritis the aim of the reduction of body weight while dieting.
- Avoidance dress warmly and stay dry.
- Mandatory rehabilitation treatment of acute joint trauma until healed full.
- Clinical observation during symptoms of osteoarthritis.


































